Cybersecurity researchers have uncovered weaknesses in Sonos sensible audio system that could possibly be exploited by malicious actors to clandestinely snoop on customers.
The vulnerabilities “led to a complete break within the safety of Sonos’s safe boot course of throughout a variety of units and remotely with the ability to compromise a number of units over the air,” NCC Group safety researchers Alex Plaskett and Robert Herrera mentioned.
Profitable exploitation of one among these flaws might enable a distant attacker to acquire covert audio seize from Sonos units via an over-the-air assault. They affect all variations previous to Sonos S2 launch 15.9 and Sonos S1 launch 11.12, which have been shipped in October and November 2023.
The findings have been offered at Black Hat USA 2024. An outline of the 2 safety defects is as follows –
- CVE-2023-50809 – A vulnerability within the Sonos One Gen 2 Wi-Fi stack doesn’t correctly validate an data aspect whereas negotiating a WPA2 four-way handshake, resulting in distant code execution
- CVE-2023-50810 – A vulnerability within the U-Boot element of the Sonos Period-100 firmware that might enable for persistent arbitrary code execution with Linux kernel privileges
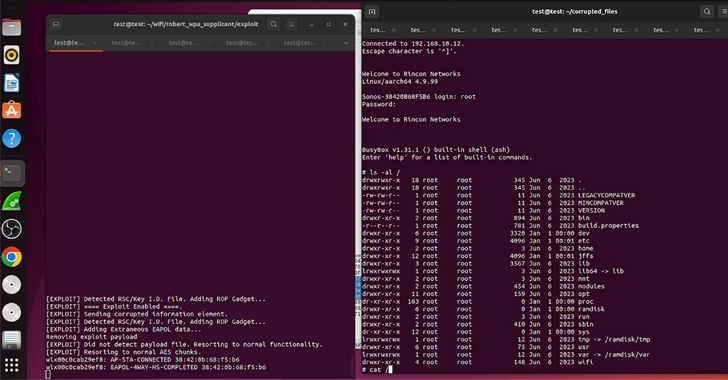
NCC Group, which reverse-engineered the boot course of to attain distant code execution on Sonos Period-100 and the Sonos One units, mentioned CVE-2023-50809 is the results of a reminiscence corruption vulnerability within the Sonos One’s wi-fi driver, which is a third-party chipset manufactured by MediaTek.
“In wlan driver, there’s a doable out of bounds write attributable to improper enter validation,” MediaTek mentioned in an advisory for CVE-2024-20018. “This might result in native escalation of privilege with no extra execution privileges wanted. Consumer interplay is just not wanted for exploitation.”
The preliminary entry obtained on this method paves the best way for a sequence of post-exploitation steps that embrace acquiring a full shell on the gadget to achieve full management over the sensible speaker within the context of root adopted by deploying a novel Rust implant able to capturing audio from the microphone inside shut bodily proximity to the speaker.
The opposite flaw, CVE-2023-50810, pertains to a series of vulnerabilities recognized within the safe boot course of to breach Period-100 units, successfully making it doable to bypass safety controls to permit for unsigned code execution within the context of the kernel.

This might then be mixed with an N-day privilege escalation flaw to facilitate ARM EL3 stage code execution and extract hardware-backed cryptographic secrets and techniques.
“General, there are two necessary conclusions to attract from this analysis,” the researchers mentioned. “The primary is that OEM parts should be of the identical safety commonplace as in-house parts. Distributors also needs to carry out menace modeling of all of the exterior assault surfaces of their merchandise and be certain that all distant vectors have been topic to adequate validation.”
“Within the case of the safe boot weaknesses, then you will need to validate and carry out testing of the boot chain to make sure that these weaknesses will not be launched. Each {hardware} and software-based assault vectors needs to be thought of.”
The disclosure comes as firmware safety firm Binarly revealed that lots of of UEFI merchandise from almost a dozen distributors are inclined to a crucial firmware provide chain subject often called PKfail, which permits attackers to bypass Safe Boot and set up malware.
Particularly, it discovered that lots of of merchandise use a take a look at Platform Key generated by American Megatrends Worldwide (AMI), which was seemingly included of their reference implementation in hopes that it could get replaced with one other safely-generated key by downstream entities within the provide chain.
“The issue arises from the Safe Boot ‘grasp key,’ often called the Platform Key (PK) in UEFI terminology, which is untrusted as a result of it’s generated by Unbiased BIOS Distributors (IBVs) and shared amongst completely different distributors,” it mentioned, describing it as a cross-silicon subject affecting each x86 and ARM architectures.
“This Platform Key […] is usually not changed by OEMs or gadget distributors, leading to units transport with untrusted keys. An attacker with entry to the personal a part of the PK can simply bypass Safe Boot by manipulating the Key Alternate Key (KEK) database, the Signature Database (db), and the Forbidden Signature Database (dbx).”
Because of this, PKfail permits dangerous actors to run arbitrary code in the course of the boot course of, even with Safe Boot enabled, permitting them to signal malicious code and ship a UEFI bootkit, akin to BlackLotus.
“The primary firmware weak to PKfail was launched again in Could 2012, whereas the most recent was launched in June 2024,” Binarly mentioned. “General, this makes this supply-chain subject one of many longest-lasting of its sort, spanning over 12 years.”