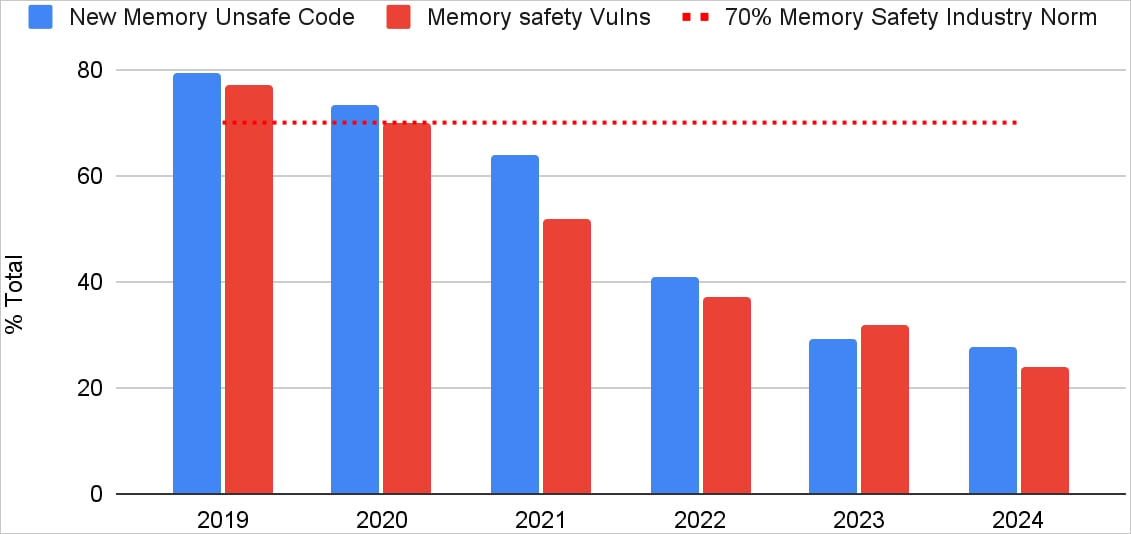
The share of Android vulnerabilities attributable to reminiscence questions of safety has dropped from 76% in 2019 to solely 24% in 2024, representing an enormous lower of over 68% in 5 years.
That is properly beneath the 70% beforehand present in Chromium, making Android a superb instance of how a big challenge can steadily and methodically transfer to a secure territory with out breaking backward compatibility.
Google says it achieved this consequence by prioritizing new code to be written in memory-safe languages like Rust, minimizing the introduction of latest flaws with time.
On the similar time, the previous code was maintained with minimal modifications centered on necessary safety fixes relatively than performing in depth rewrites that will additionally undermine interoperability.
“Based mostly on what we have realized, it is turn into clear that we don’t have to throw away or rewrite all our present memory-unsafe code,” reads Google’s report.
“As a substitute, Android is specializing in making interoperability secure and handy as a major functionality in our reminiscence security journey.”
Supply: Google
This technique makes older code mature and turns into safer over time, lowering the variety of memory-related vulnerabilities in it no matter what language it was written in.
These two pillars within the Android constructing technique had a synergistic impact in direction of the dramatic lower of reminiscence flaws on the planet’s most generally used cellular platform.
Google explains that, whereas it could appear dangerous to depart older code basically unchanged and although new code is anticipated to be higher examined and reviewed, the other is occurring, regardless of how counter-intuitive it could appear.
It is because latest code modifications introduce most flaws, so new code nearly all the time incorporates safety issues. On the similar time, bugs in older code are ironed out except builders carry out in depth modifications to it.
Supply: Google
Google says that the business, together with itself, has gone by way of 4 foremost levels in coping with reminiscence security flaws, summarized as follows:
- Reactive patching: Initially, the main target was on fixing vulnerabilities after they have been found. This strategy resulted in ongoing prices, with frequent updates wanted and customers remaining susceptible within the meantime.
- Proactive mitigations: The following step was implementing methods to make exploits tougher (e.g., stack canaries, control-flow integrity). Nevertheless, these measures typically got here with efficiency trade-offs and led to a cat-and-mouse sport with attackers.
- Proactive vulnerability discovery: This era concerned utilizing instruments like fuzzing and sanitizers to seek out vulnerabilities proactively. Whereas useful, this technique solely addressed signs, requiring fixed consideration and energy.
- Excessive-assurance prevention (Secure Coding): The newest strategy emphasizes stopping vulnerabilities on the supply through the use of memory-safe languages like Rust. This “safe by design” technique offers scalable and long-term assurance, breaking the cycle of reactive fixes and dear mitigations.
“Merchandise throughout the business have been considerably strengthened by these approaches, and we stay dedicated to responding to, mitigating, and proactively looking for vulnerabilities,” defined Google.
“Having mentioned that, it has turn into more and more clear that these approaches will not be solely inadequate for reaching an appropriate degree of danger within the memory-safety area, however incur ongoing and growing prices to builders, customers, companies, and merchandise.
“As highlighted by quite a few authorities businesses, together with CISA, of their secure-by-design report, “solely by incorporating safe by design practices will we break the vicious cycle of continually creating and making use of fixes.”
Final June, the U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Safety Company (CISA) warned that 52% of probably the most broadly used open-source tasks use memory-unsafe languages.
Even tasks written in memory-safe languages typically rely upon elements written in memory-unsafe languages, so the safety danger is difficult to deal with.
CISA advisable that software program builders write new code in memory-safe languages reminiscent of Rust, Java, and GO and transition present tasks, particularly crucial elements, to these languages.









