Fortinet publicly disclosed at the moment a crucial FortiManager API vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2024-47575, that was exploited in zero-day assaults to steal delicate recordsdata containing configurations, IP addresses, and credentials for managed gadgets.
The corporate privately warned FortiManager prospects in regards to the flaw beginning October thirteenth in superior notification emails seen by BleepingComputer that contained steps to mitigate the flaw till a safety replace was launched.
Nonetheless, information of the vulnerability started leaking on-line all through the week by prospects on Reddit and by cybersecurity researcher Kevin Beaumont on Mastodon, who calls this flaw “FortiJump.”
Fortinet machine admins have additionally shared that this flaw has been exploited for some time, with a buyer reporting being attacked weeks earlier than the notifications have been despatched to prospects.
“We obtained breached on this one weeks earlier than it hit “advance notifications” – 0-day I assume,” reads a now-deleted touch upon Reddit.
FortiManager zero-day disclosed
At the moment, Fortinet publicly disclosed the actively exploited crucial FortiManager flaw, tracked as CVE-2024-47575 with a rated severity of 9.8 out of 10.
“A lacking authentication for crucial operate vulnerability [CWE-306] in FortiManager fgfmd daemon could permit a distant unauthenticated attacker to execute arbitrary code or instructions through specifically crafted requests,” reads Fortinet’s FG-IR-24-423 safety advisory.
“Stories have proven this vulnerability to be exploited within the wild.”
A supply conversant in the assaults informed BleepingComputer that the advisory is lacking some crucial info to take advantage of the bug: risk actors should first extract a sound certificates from any owned or compromised Fortinet gadgets, together with FortiManager VM.
The flaw impacts the next FortiManager variations:
| Model | Affected | Resolution |
|---|---|---|
| FortiManager 7.6 | 7.6.0 | Improve to 7.6.1 or above |
| FortiManager 7.4 | 7.4.0 via 7.4.4 | Improve to 7.4.5 or above |
| FortiManager 7.2 | 7.2.0 via 7.2.7 | Improve to 7.2.8 or above |
| FortiManager 7.0 | 7.0.0 via 7.0.12 | Improve to 7.0.13 or above |
| FortiManager 6.4 | 6.4.0 via 6.4.14 | Improve to six.4.15 or above |
| FortiManager 6.2 | 6.2.0 via 6.2.12 | Improve to six.2.13 or above |
| FortiManager Cloud 7.6 | Not affected | Not Relevant |
| FortiManager Cloud 7.4 | 7.4.1 via 7.4.4 | Improve to 7.4.5 or above |
| FortiManager Cloud 7.2 | 7.2.1 via 7.2.7 | Improve to 7.2.8 or above |
| FortiManager Cloud 7.0 | 7.0.1 via 7.0.12 | Improve to 7.0.13 or above |
| FortiManager Cloud 6.4 | 6.4 all variations | Migrate to a set launch |
At the moment, solely FortiManager variations 7.2.8 and seven.4.5 have been launched however BleepingComputer discovered that the remainder can be launched within the upcoming days.
Fortinet created the “FortiGate to FortiManager Protocol” (FGFM) to permit corporations to simply deploy FortiGate firewall gadgets and have them register with a distant FortiManager server to allow them to be managed from a central location.
“The FortiGate to FortiManager (FGFM) protocol is designed for FortiGate and FortiManager deployment situations, particularly the place NAT is used,” reads documentation in regards to the FGFM protocol.
“These situations embrace the FortiManager on public web whereas the FortiGate unit is behind NAT, FortiGate unit is on public web whereas FortiManager is behind NAT, or each FortiManager and FortiGate unit have routable IP addresses.”
As cybersecurity researcher Kevin Beaumont factors out, it’s not troublesome for an attacker to attach a FortiGate machine to an uncovered FortiManager server so long as they’ve obtained a sound certificates.
This certificates is used to arrange an SSL tunnel between the FortiGate and the FortiManager server to authenticate each gadgets. Nonetheless, a supply conversant in the vulnerability informed BleepingComputer that this isn’t the place the vulnerability lies.
As a substitute, a further degree of authorization is required to execute instructions through the FortiManager FGFM API, which could be bypassed utilizing the CVE-2024-47575 flaw. The authentication bypass within the API has been mounted within the newest variations of FortiManager.
This API permits attackers to execute instructions, retrieve info, and take full management over managed gadgets and FortiManager to realize additional entry to company networks.
“As a result of MSPs — Managed Service Suppliers — typically use FortiManager, you should utilize this to enter inside networks downstream,” warned Beaumont.
“Due to the best way FGFM is designed — NAT traversal conditions — it additionally means in the event you achieve entry to a managed FortiGate firewall you then can traverse as much as the managing FortiManager machine… after which again all the way down to different firewalls and networks.”
Fortinet has provided other ways to mitigate this assault if it’s not doable to put in the newest firmware replace right now:
- Make the most of the set fgfm-deny-unknown allow command to stop gadgets with unknown serial numbers from registering to the FortiManager.
- Create a customized certificates to be used when creating the SSL tunnel and authenticating FortiGate gadgets with FortiManager.
Nonetheless, Fortinet warns that if a risk actor is ready to get hold of this certificates, then it may nonetheless be used to attach FortiGate gadgets and exploit the flaw.
- Create an allowed listing of IP addresses for FortiGate gadgets which might be allowed to attach.
Directions on the best way to carry out these mitigations and restore compromised servers could be present in Fortinet’s advisory.
Exploited to steal knowledge
Fortinet says the noticed assaults have been used to steal varied recordsdata from the FortiManager server that “contained the IPs, credentials and configurations of the managed gadgets.”
This stolen info can be utilized to study and goal FortiGate gadgets to realize preliminary entry to company networks or MSPs downstream purchasers.
The corporate additionally confirms there isn’t a proof of malware put in on compromised FortiManager providers or configuration adjustments to managed FortiGate gadgets.
“At this stage, now we have not acquired experiences of any low-level system installations of malware or backdoors on these compromised FortiManager methods,” Fortinet says within the safety advisory.
“To one of the best of our information, there have been no indicators of modified databases, or connections and modifications to the managed gadgets.”
Fortinet has not attributed the assaults to any specific risk actor and isn’t sharing any details about what number of and the kind of prospects that have been impacted because of the ongoing investigation.
Nonetheless, Fortinet has shared the next IOCs to assist safety professionals and community admins detect whether or not their FortiManager servers have been breached utilizing this vulnerability.
The noticed assaults present that the risk actors related attacker-controlled FortiGate gadgets below the title “localhost,” which can seem within the Unregistered Units part in Fortimanager.
Log entries will present that the risk actors issued API instructions so as to add these unregistered “localhost” gadgets:
sort=occasion,subtype=dvm,pri=info,desc="Gadget,supervisor,generic,info,log",consumer="machine,...",msg="Unregistered machine localhost add succeeded" machine="localhost" adom="FortiManager" session_id=0 operation="Add machine" performed_on="localhost" adjustments="Unregistered machine localhost add succeeded"
One other log entry shared by Fortinet was used to edit machine settings:
sort=occasion,subtype=dvm,pri=discover,desc="Gadget,Supervisor,dvm,log,at,discover,degree",consumer="System",userfrom="",msg="" adom="root" session_id=0 opera,on="Modify machine" performed_on="localhost" adjustments="Edited machine settings (SN FMG-VMTM23017412)"
Fortinet says that rogue FortiGate gadgets have been seen utilizing the serial quantity FMG-VMTM23017412, which seems to be the format utilized by FortiGate-VM digital machines.
Different IOCs embrace the creation of the /tmp/.tm and /var/tmp/.tm recordsdata.
The next IP addresses have been noticed within the assaults, all situated on the cloud internet hosting firm, Vultr:
- 45.32.41.202
- 104.238.141.143 (Not too long ago seen internet hosting SuperShell C2 infrastructure)
- 158.247.199.37
- 45.32.63.2
The SuperShell C2 framework was not too long ago utilized in assaults on F5 BIG-IP routers that have been attributed with average confidence to a Chinese language (PRC) risk actor referred to as UNC5174.
Fortinet warns that not all IOCs could also be current on exploited gadgets.
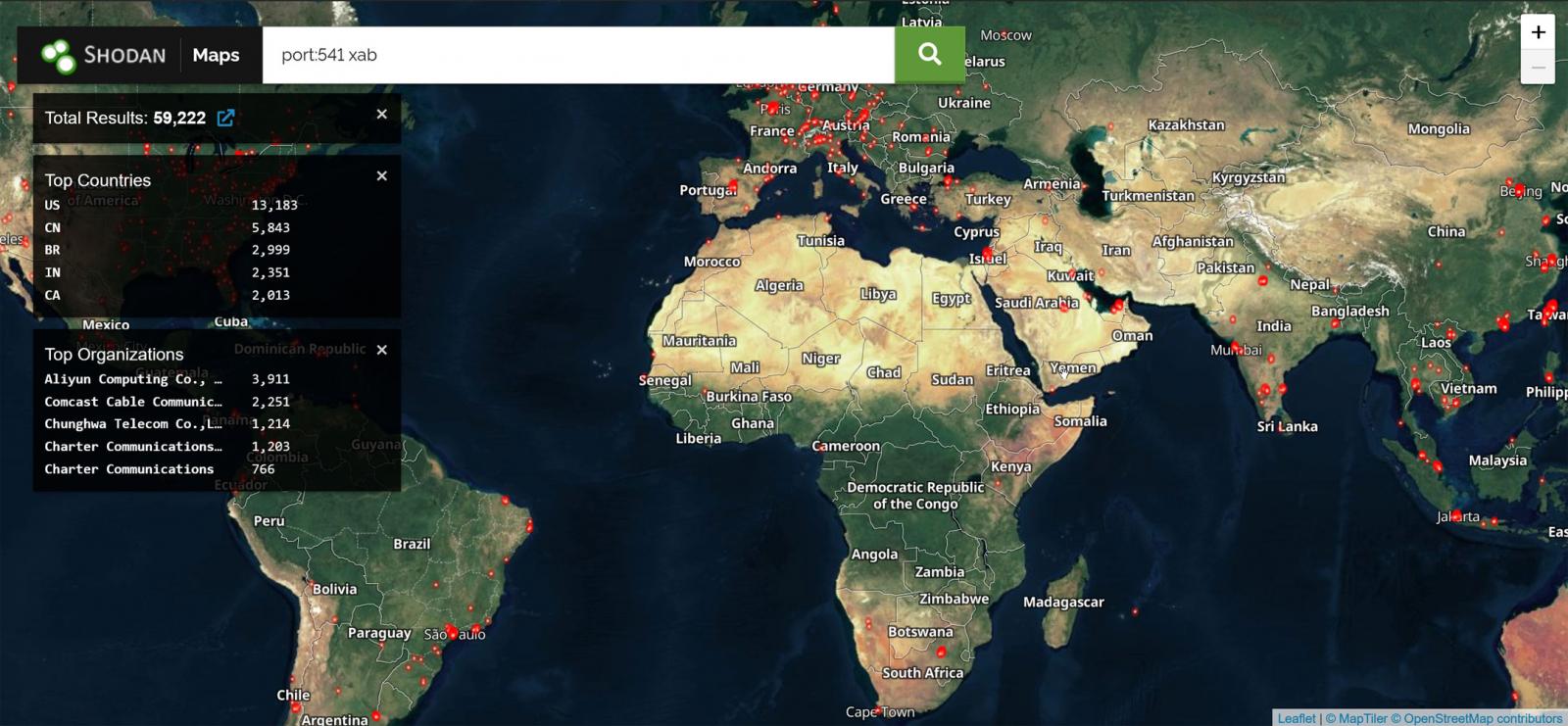
Beaumont warns {that a} Shodan search exhibits there are 59,534 FortiManager gadgets whose FGFM ports (TCP port 531) are uncovered on-line, with the bulk within the US.
Personal disclosure results in frustration
Fortinet shared the next assertion with BleepingComputer in regards to the CVE-2024-47575 flaw and the way it was disclosed to prospects.
“After figuring out this vulnerability (CVE-2024-47575), Fortinet promptly communicated crucial info and sources to prospects. That is in keeping with our processes and finest practices for accountable disclosure to allow prospects to strengthen their safety posture previous to an advisory being publicly launched to a broader viewers, together with risk actors. We even have printed a corresponding public advisory (FG-IR-24-423) reiterating mitigation steering, together with a workaround and patch updates. We urge prospects to comply with the steering supplied to implement the workarounds and fixes and to proceed monitoring our advisory web page for updates. We proceed to coordinate with the suitable worldwide authorities businesses and business risk organizations as a part of our ongoing response.”
❖ Fortinet.
Nonetheless, Fortinet prospects have expressed frustration over how the vulnerability was disclosed, with some FortiManager prospects not receiving the superior discover and having to depend on leaked info to search out out in regards to the zero-day vulnerability.
“How do I get on the personal disclosure e mail listing? I’ve 7.2.7 and didn’t hear about this,” a FortiManager buyer commented on Reddit.
BleepingComputer was informed that each one FortiManager prospects ought to have acquired this notification to their “Grasp” account. If they didn’t, they need to contact Fortinet or their reseller to verify they’ve the proper contact info.
Others have been pissed off that the personal advisory didn’t listing FortiManager Cloud as impacted by the zero-day, but once they referred to as Fortinet TAC, they have been informed it was impacted.
This flaw is just not the primary time Fortinet determined to quietly patch a crucial vulnerability or privately disclose it to prospects.
In December 2022, Fortinet quietly patched an actively exploited FortiOS SSL-VPN vulnerability tracked as CVE-2022-42475 with out publicly stating that the flaw was utilized in assaults. Like this FortiManager flaw, Fortinet issued a non-public TLP:Amber advisory to prospects on December seventh, alerting prospects to the bug.
In June 2023, Fortinet once more quietly patched a crucial FortiGate SSL-VPN distant code execution vulnerability tracked as CVE-2023-27997 on June 8. 4 days later, on June eleventh, the corporate disclosed that the flaw had been utilized in zero-day assaults in opposition to authorities, manufacturing, and demanding infrastructure.
Some have referred to as out Fortinet’s lack of transparency, recalling an October 2023 submit from Fortinet that said, “the safety neighborhood should normalize transparency and data sharing for organizations to collectively advance their battle in opposition to adversaries.”
Replace 10/23/24: Up to date impacted variations and added additional details about the vulnerability.









