The favored open supply challenge, ‘ip’ lately had its GitHub repository archived, or made “read-only” by its developer.
Fedor Indutny, on account of a CVE report filed towards his challenge, began getting hounded by folks on the web bringing the vulnerability to his consideration.
Sadly, Indutny’s case is not remoted. In current instances, open-source builders have been met with an uptick in receiving debatable or, in some instances, outright bogus CVE stories filed for his or her initiatives with out affirmation.
This may result in unwarranted panic among the many customers of those initiatives and alerts being generated by safety scanners, all of which flip right into a supply of headache for builders.
‘node-ip’ GitHub repository archived
Earlier this month, Fedor Indutny who’s the creator of the ‘node-ip’ challenge archived the challenge’s GitHub repository successfully making it read-only, and limiting the flexibility of individuals to open new points (discussions), pull requests, or submit feedback to the challenge.
The ‘node-ip’ challenge exists on the npmjs.com registry because the ‘ip’ bundle which scores 17 million downloads weekly, making it one of the vital fashionable IP tackle parsing utilities in use by JavaScript builders.
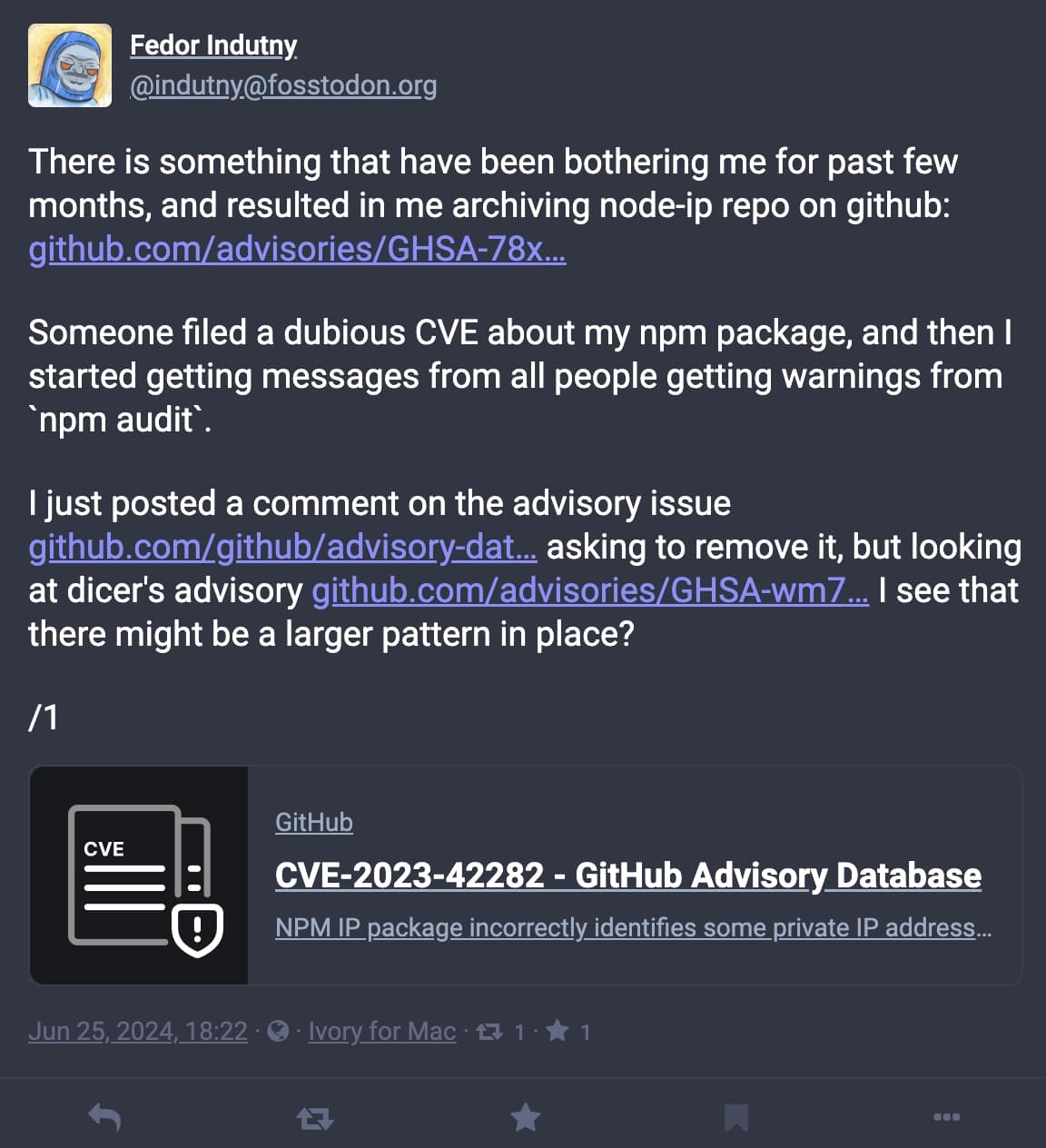
On Tuesday, June twenty fifth, Indutny took to social media to voice his reasoning behind archiving ‘node-ip’:
“There’s something which have [sic] been bothering me for previous few months, and resulted in me archiving node-ip repo on GitHub,” posted the developer by way of his Mastodon account.
It has to do with CVE-2023-42282, a vulnerability disclosed within the challenge earlier this 12 months.
“Somebody filed a doubtful CVE about my npm bundle, after which I began getting messages from all folks getting warnings from ‘npm audit’,” states the developer in the identical submit.
Node.js builders utilizing different open initiatives, similar to npm packages and dependencies of their utility can run the “npm audit” command to verify if any of those initiatives utilized by their utility have had vulnerabilities reported towards them.
The CVE has to do with the utility not appropriately figuring out personal IP addresses provided to it in a non-standard format, similar to hexadecimal. This may trigger the ‘node-ip’ utility to deal with a personal IP tackle (in hex format) similar to ” 0x7F.1…” (which represents 127.1…) as public.
Ought to an utility rely solely on node-ip to verify if a offered IP tackle is public, non-standard inputs may cause inconsistent outcomes to be returned by the affected variations of the utility.
‘Doubtful’ safety influence
Public sources recommend that CVE-2023-42282 had initially been scored as a 9.8 or “vital.”
Though Indutny did certainly repair the difficulty in later variations of his challenge, he disputed that the bug constituted an precise vulnerability and that too of an elevated severity.
“I imagine that the safety influence of the bug is relatively doubtful,” the developer earlier wrote, requesting GitHub to revoke the CVE.
“Whereas I did not actually intend the module for use for any safety associated checks, I am very curious how an untrusted enter may find yourself being handed into ip.isPrivate or ip.isPublic [functions] after which used for verifying the place the community connection got here from.”
Disputing a CVE isn’t any simple job both, as a GitHub safety group member defined. It requires a challenge maintainer to chase the CVE Numbering Authorities (CNA) that had initially issued the CVE.
CNAs have conventionally comprised NIST’s NVD and MITRE. Over the previous few years, know-how firms and safety distributors joined the checklist and are additionally capable of problem CVEs at will.
These CVEs, together with the vulnerability description and the reported severity ranking, are then syndicated and republished by different safety databases, similar to GitHub advisories.
Following Indutny’s submit on social media, GitHub lowered the severity of the CVE of their database and prompt the developer activate personal vulnerability reporting to higher handle incoming stories and minimize noise.
On the time of writing, the vulnerability’s severity on NVD stays “vital.”
A rising nuisance
The CVE system, initially designed to assist safety researchers ethically report vulnerabilities in a challenge and catalog these after accountable disclosure, has these days attracted a phase of group members submitting unverified stories.
Whereas many of the CVEs are filed in good religion by accountable researchers and symbolize credible safety vulnerabilities, a lately rising sample includes beginner safety fanatics and bug bounty hunters ostensibly “accumulating” CVEs to counterpoint their resume relatively than reporting safety bugs that represent real-world, sensible influence from exploitation.
Consequently, builders and challenge maintainers have pushed again.
In September 2023, Daniel Stenberg, creator of the well-known software program challenge ‘curl’ rebuked the “bogus curl problem CVE-2020-19909,” a Denial of Service bug reported towards the challenge.
Initially scored as a 9.8 or vital in severity per NVD’s historical past, the now-disputed CVE has had its ranking dropped to a “low” 3.3 after discussions ensued questioning the tangible safety influence of the flaw.
“This was not a novel occasion and it was not the primary time it occurred. This has been occurring for years,” Stenberg wrote criticizing the CVE entry.
“I’m not a fan of philosophical thought workout routines round vulnerabilities.”
“They’re distractions from the true issues and I discover them relatively pointless. It’s straightforward to check how this flaw performs out on quite a few platforms utilizing quite a few compilers.”
“It is not a safety drawback on any of them.”
In response to Stenberg, the technical particulars of the “foolish bug” meant it may end in sudden habits, not a safety flaw that might be abused.
Yet one more npm challenge, micromatch which will get 64 million weekly downloads has had ‘excessive’ severity ReDoS vulnerabilities reported towards it with its creators being chased by group members inquiring concerning the points.
“Are you able to level out a minimum of one library that implements micromatch or braces that’s vulnerable to the vulnerability so we will see the way it’s truly a vulnerability in the true world, and never simply theoretical?” requested Jon Schlinkert, reacting to CVE-2024-4067 filed for his challenge, micromatch.
In the identical thread, the developer, apparently after failing to obtain a passable proof of idea exploit from the vulnerability reporter responded with:
“I get these points on a regular basis for issues that may’t even be a vulnerability except you do it to your self. Like regex in low stage libraries that can by no means be accessible to a browser, except you are letting customers submit common expressions in an online type which might be simply utilized by your utility.”
“I requested for examples of how a real-world library would encounter these ‘vulnerabilities’ and also you by no means responding with an instance.”
I too, lately messaged micromatch builders after a third social gathering knowledgeable us of a possible “threat” posed by the challenge, because it appeared just like the accountable factor to do on the time.
Sadly, versus representing an exploitable vulnerability, it ended up being a nuisance report (very similar to CVE-2024-4067) that builders had already been chased about.
Different than simply being an annoyance for challenge maintainers, the act of getting CVEs issued for unverified vulnerability stories is akin to stirring up a Denial of Service (DoS) towards a challenge, its creators, and its wider shopper base, and for good causes.
Developer safety options (similar to npm audit) that are designed to forestall susceptible elements from reaching your functions might set off alerts if any recognized vulnerabilities are detected and relying in your settings, break your builds.
“Jackson had this drawback a number of months again, the place somebody reported a vital CVE towards the challenge and broke builds throughout the planet,” a commentator had written in 2023, reacting to the bogus curl CVE.
Moderately than being a safety drawback with the challenge, as different builders acknowledged, the difficulty represented the inherent nature of recursive Java knowledge constructions.
The place is the stability?
Recurring incidents like these increase the query, how does one strike a stability?
Relentlessly reporting theoretical vulnerabilities can depart open-source builders, many of who’re volunteers, exhausted from triaging noise.
On the flip facet, wouldn’t it be moral if safety practitioners, together with novices, sat on what they thought was a safety flaw—in order to not inconvenience the challenge maintainers?
A 3rd drawback arises for initiatives with out an lively maintainer. Deserted software program initiatives that haven’t been touched in years comprise vulnerabilities that, even when disclosed, won’t ever be mounted and there exists no means to contact their unique maintainer.
In such instances, intermediaries together with CNAs and bug bounty platforms are left in limbo.
On receiving a vulnerability report from a researcher, these organizations might not at all times be capable to sufficiently vet each such report independently. With out listening to from the (now absent) challenge maintainers, they could be compelled to assign and publish CVEs after the “accountable disclosure” window has elapsed.
No easy reply exists to those issues simply but.
Till the safety analysis, developer, and vendor communities come collectively to determine an efficient resolution, builders are sure to get pissed off with bogus stories burning them out, and the CVE system changing into flooded with exaggerated “vulnerabilities” that will look credible on paper however are successfully moot.









