A newly found malware marketing campaign has been discovered to focus on personal customers, retailers, and repair companies primarily positioned in Russia to ship NetSupport RAT and BurnsRAT.
The marketing campaign, dubbed Horns&Hooves by Kaspersky, has hit greater than 1,000 victims because it started round March 2023. The top purpose of those assaults is to leverage the entry afforded by these trojans to put in stealer malware similar to Rhadamanthys and Meduza.
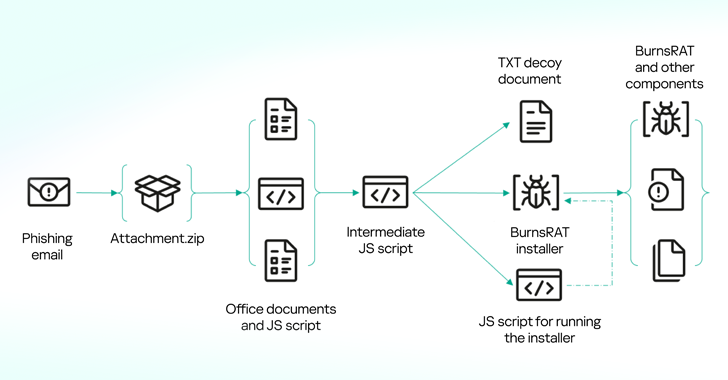
“Current months have seen a surge in mailings with lookalike e-mail attachments within the type of a ZIP archive containing JScript scripts,” safety researcher Artem Ushkov mentioned in a Monday evaluation. “The script information [are] disguised as requests and bids from potential prospects or companions.”
The risk actors behind the operations have demonstrated their energetic improvement of the JavaScript payload, making important adjustments throughout the course of the marketing campaign.
In some cases, the ZIP archive has been discovered to comprise different paperwork associated to the group or particular person being impersonated in order to extend the chance of success of the phishing assault and dupe recipients into opening the malware-laced file.
One of many earliest samples recognized as a part of the marketing campaign is an HTML Utility (HTA) file that, when run, downloads a decoy PNG picture from a distant server utilizing the curl utility for Home windows, whereas additionally stealthily retrieving and operating one other script (“bat_install.bat”) from a special server utilizing the BITSAdmin command-line instrument.
The newly downloaded script then proceeds to fetch utilizing BITSAdmin a number of different information, together with the NetSupport RAT malware, which establishes contact with a command-and-control (C2) server arrange by the attackers.

A subsequent iteration of the marketing campaign noticed in mid-Might 2023 concerned the intermediate JavaScript mimicking reputable JavaScript libraries like Subsequent.js to activate the NetSupport RAT an infection chain.
Kaspersky mentioned it additionally discovered one other variant of the JavaScript file that dropped an NSIS installer that is then chargeable for deploying BurnsRAT on the compromised host.
“Though the backdoor helps instructions for remotely downloading and operating information, in addition to varied strategies of executing instructions through the Home windows command line, the primary job of this element is to start out the Distant Manipulator System (RMS) as a service and ship the RMS session ID to the attackers’ server,” Ushkov defined.
“RMS is an utility that permits customers to work together with distant techniques over a community. It offers the flexibility to handle the desktop, execute instructions, switch information and change information between gadgets positioned in several geographic areas.”
In an indication that the risk actors continued to tweak their modus operandi, two different assault sequences noticed in late Might and June 2023 got here with a very reworked BAT file for putting in NetSupport RAT and integrated the malware immediately throughout the JavaScript code, respectively.
There are indications that the marketing campaign is the work of a risk actor often called TA569 (aka Gold Prelude, Mustard Tempest, and Purple Vallhund), which is understood for working the SocGholish (aka FakeUpdates) malware. This connection stems from overlaps within the NetSupport RAT license and configuration information utilized in respective actions.
It is price mentioning that TA569 has additionally been identified to behave as an preliminary entry dealer for follow-on ransomware assaults similar to WastedLocker.
“Relying on whose fingers this entry falls into, the implications for sufferer firms can vary from information theft to encryption and harm to techniques,” Ushkov mentioned. “We additionally noticed makes an attempt to put in stealers on some contaminated machines.”